DIN 3325 Stainless Steel Rising Stem Gate Valve
DIN 3325 Stainless Steel Rising Stem Gate Valve Specification: Size: DN15 – DN1200 Model:Z40H Type: Rising Stem and Wedge Single Disc, Solid or Flexible Wedge, Flat Gate. Operation: Handwheel, Gear Worm, Electric Operated  Standard: Face to Face Std.: GB/T12221, DIN3202, etc. End Connection Std.: JB/T79, DIN2543-2550, GOST 12820-80, etc. Test Standard: ISO5208, API 600, BS 6755
Transmission spare parts for XCMG , LIUGONG, SDLG, XGMA, DEGONG, SHANTUI wheel loader, excavator spare parts with best price.
wheel loader spare parts ZF 4WG200 4WG180 transmission
Basic terminology for transmission: Transmission Box,Wheel Loader Transmission Assy,Transmission Gear Selector,Transmission Oil Radiator Jinan Union Construction Machinery Co., Ltd. , https://www.tfloaderparts.com
Pressure: PN16 – PN250
Material: 1.0619/GP240GH/GS-C25(WCB), 1.7357 (WC6), 1.7379/1.7382(WC9), 1.7363 (C5), 1.7389 (C12), 1.4308(CF8), 1.4408(CF8M), 1.4552(CF8C). Etc.
Design & Manufacture Std.: GB/T12234, DIN3352, GOST 12820-80, etc.
Product: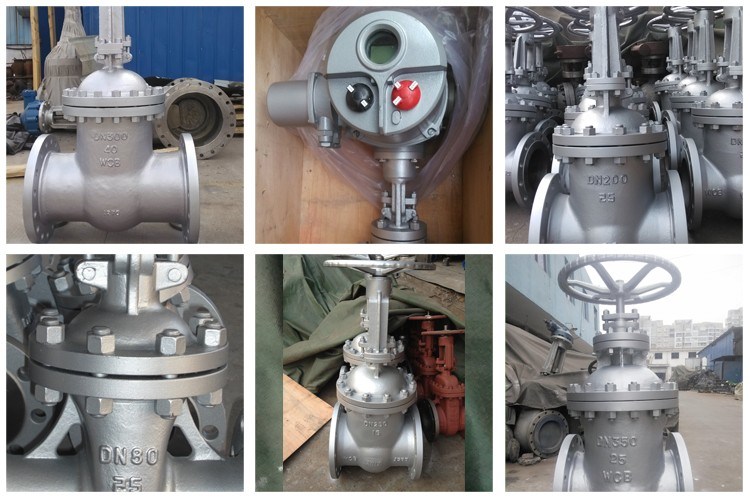
Production Process: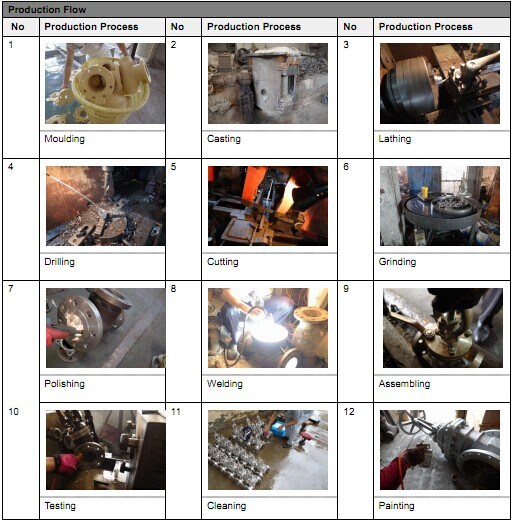
Packaging:
  

NO.
Part Name
Material
01
Body
ASTM A216 WCB
GS-C25, CF8, CF8M
02
Seat Ring
ASTM A216 + 13Cr
Â
03
Wedge
ASTM A216 + 13Cr
Â
04
Stem
ASTM A276 420
13Cr, F304, F316
05
Gasket
304 + Graphite
GS-C25, CF8, CF8M
06
Bonnet
ASTM A216 WCB
Â
07
Stud
ASTM A193 B7
ASTM A193-B8
08
Nut
ASTM A194 2H
ASTM A194-8
09
Backseat
ASTM A216 + 13Cr
Â
10
Stud
ASTM A193 B7
Â
11
Nut
ASTM A194 2H
Â
12
Yoke
ASTM A216 WCB
Â
13
Packing
Graphite
Â
14
Pin
ASTM A276 410
C.S, SS304, SS316
15
Gland Bolt
ASTM A193 B7
Â
16
Gland Nut
ASTM A194 2H
Â
17
Bushing
ASTM A276 410
Â
18
Gland
ASTM A216 WCB
Â
19
Bearing
ASTM A29
A105, F304, F316
20
Stem Nut
ZCuAl10Fe3 Bronze
Bronze, SS304, SS316
21
Lubricator
Cu
Brass
22
Retaining Nut
C.S
Â
23
Handwheel
ASTM A47
A105, F304, F316
24
H.W. Lock Nut
C.S
25#, SS304, SS316
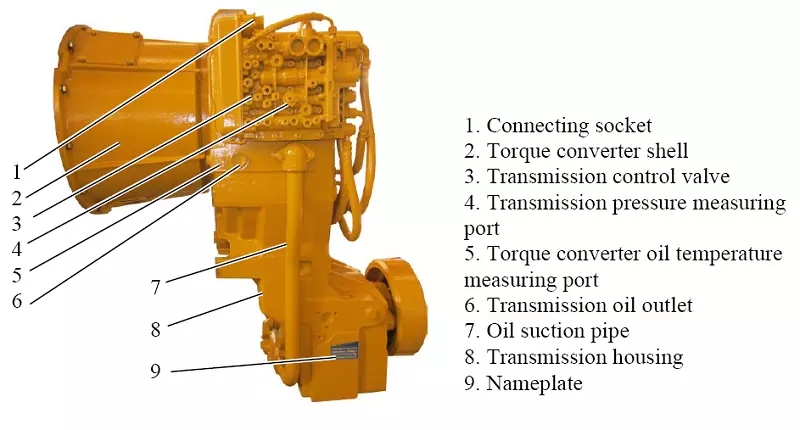
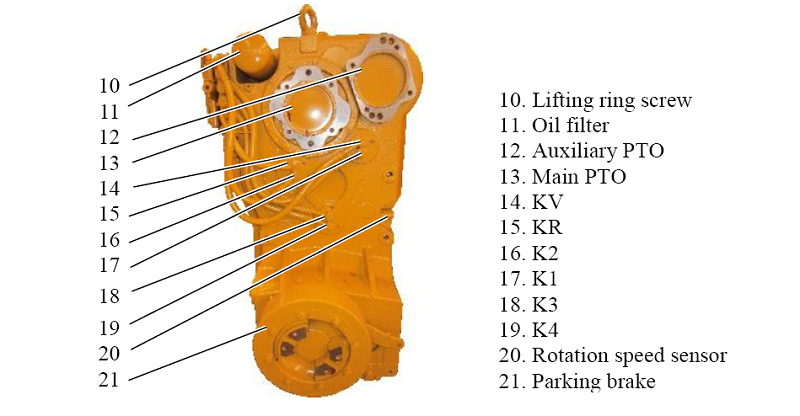
(1) Driving gear and driven gear. The input shaft can be understood as connected to the clutch and rotates under the drive of the Engine. The gear fixed on the input shaft rotates accordingly. This gear is called the driving gear and the gear connected to the output shaft is forced to rotate. This gear is called a driven gear.
(2) Transmission ratio i. The ratio of the number of Teeth of the driven gear to the number of teeth of the driving gear is defined as the transmission ratio.
When the relationship between the number of teeth of the driven gear and the number of teeth of the driving gear changes, the transmission ratio i changes. Under the condition of constant engine speed, it will affect the output shaft speed change, that is, the wheel speed change. For a pair of gears that mesh with each other, the number of teeth will not change during use, so its transmission ratio is fixed. If a number of gears with unequal numbers of teeth are installed on the input shaft to mesh with gears with varying numbers of teeth on the output shaft, a set of stepped transmissions with different transmission ratios i can be obtained. The automobile transmission is based on this basic principle to realize the gear shift.
(3) Forward gear, a gear position that enables the car to travel forward. Reverse gear is a gear that can make the car go backwards. In neutral, all gears in the transmission are not in the working position. At this time, after the engine power is input to the input shaft, it is no longer transmitted to the output shaft.
(4) Direct files. The engine power is not transmitted by any gears in the transmission, but directly output through the transmission input shaft and the output shaft directly connected to it as a direct gear. The direct gear ratio is 1.
(5) Overdrive gear. That is, the speed of the output shaft is higher than the gear of the input shaft.
(6) Number of files. Refers to the number of gears that the stepped gear transmission has. Commonly used gear transmissions have four to five gears, and three-speed transmissions are rare. The more gears, the better the car's adaptability to driving conditions and the lower the fuel consumption. However, the more complex the transmission mechanism and the operating mechanism, the more difficult the operation and the higher the cost.
(7) Low-end and high-end. In the gears of the transmission, the gear with the smaller number is called low gear. The smaller the number, the greater the transmission ratio, the greater the traction, and the lower the vehicle speed. For example, the transmission ratio of first gear is the largest in the forward gear, the vehicle speed is the lowest, and the traction is the largest. A gear with a large number is called high-end. The larger the number, the smaller the transmission ratio and the lower the traction, but the higher the speed.
(8) Shift gears. The process of changing the transmission ratio of the transmission is called shifting. The gear shift of the adapter sleeve is integrated with the gear, and the gear ring on the tooth side meshes (or separates) with the adapter sleeve to achieve the transmission ratio change is called the adapter sleeve shift. Synchronizer shifts, use synchronizer to shift gears. Not only is there no impact and noise on the engaging teeth, but the shift time is also short.
(9) Skip gears. During the driving of the automobile, due to the wear and vibration of the coupling teeth, the coupling sleeve and the coupling ring gear are separated and the transmission is in a neutral state.